“How Do Satellites Always Stay in the Same Place in the Sky?” – In fact not all satellites do – only the ones called geosynchronous.
From our Earthling point of view, a satellite in geosynchronous orbit appears to hover over one point on Earth. The satellite is in a high orbit when it circles the Earth once a day, the same amount of time it takes the Earth to rotate on its axis. A receiving dish on Earth can point to the satellite at one spot in the sky, and the dish does not have to move to track the satellite. There are now about a couple hundred satellites in geosynchronous orbit located above the equator.
A set of rules, called Kepler’s laws, determines how far a satellite must be above the Earth’s surface to be a geosynchronous satellite. The closer an orbiting object is to the Earth, the faster it goes and the less time it takes to orbit.
So, officially …
Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at exactly the same rate as Earth. This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position. In order to perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km. This is much farther from Earth’s surface compared to many satellite
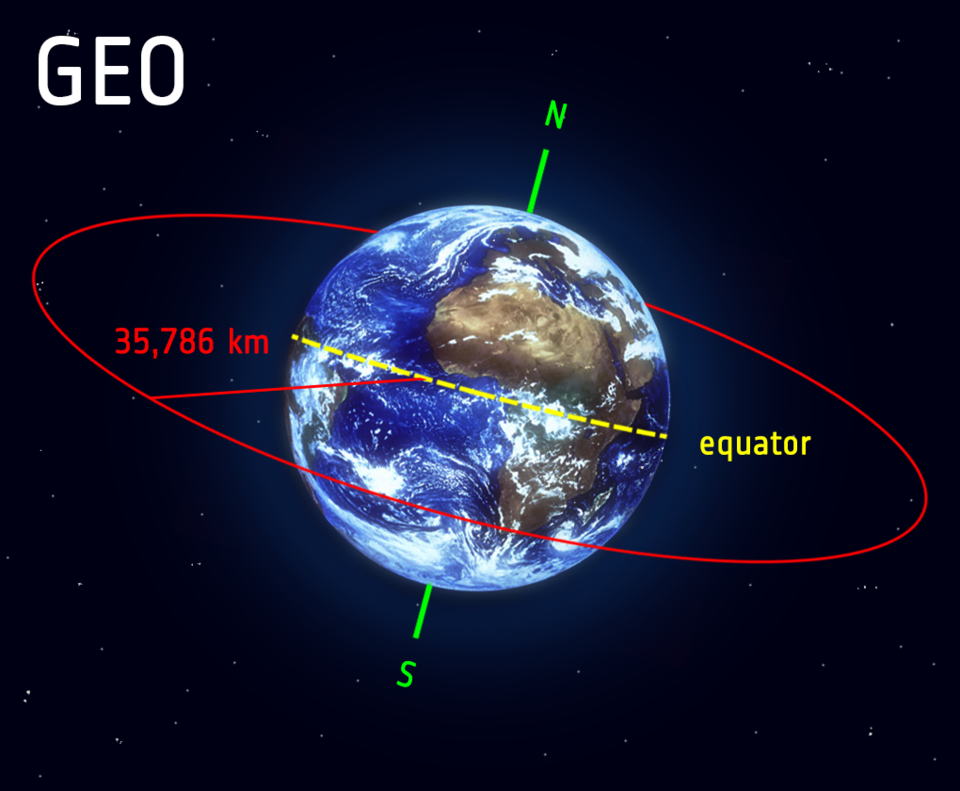
The space shuttle (when it was in service) and the International Space Station (ISS) are 250 miles high and take about 90 minutes to orbit. A geosynchronous satellite, at 22,200 miles away, takes 24 hours, or one day, to orbit. In comparison, the moon is 240,000 miles up and takes about 30 days to orbit.
If you want to track the exact location of the ISS and Hubble Space Telescope, as well as the positions of the planets then checkout heavens-above.com
It will show also show you the night sky for your location, discuss meteor showers, and list Iridium flares that you can see, too. (Iridium flares are bright flashes of light in the sky seen in the early morning or early evening, caused by reflections of the Sun off the shiny flat antennas of some sixty-six satellites owned by Iridium Communications)
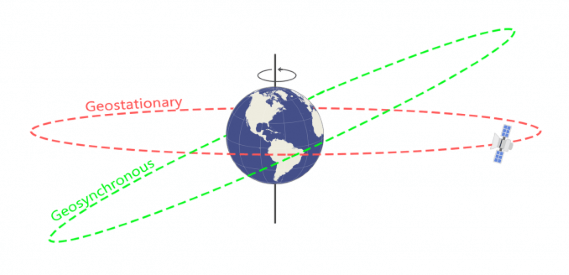
 Geosynchronous Vs Geostationary
Geosynchronous Vs Geostationary
Geosynchronous Orbits (GSO)
- a satellite whose orbital period is equal to the period of rotation of the earth (24 hrs) (satellite’s revolution is in sync with the earth’s rotation), is called a Geosynchronous Orbits
Geostationary Orbit or Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit (GEO)
- A geostationary orbit or geosynchronous equatorial orbit is a circular geosynchronous orbit above Earth’s equator and following the direction of Earth’s rotation.
- Because the satellite stays right over the same spot all the time, this kind of orbit is called “geostationary.”




You must be logged in to post a comment.